.NET Core made it easy to configure your application. Currently, I am working on a .NET 6 console application and this showed me that especially ASP.NET MVC makes it easy to set up middleware such as dependency injection. When using a console application, it is not hard but it requires a bit more work than the web application.
In this post, I would like to show you how to use .NET secrets in your .NET 6 console application.
Create a new .NET 6 console application
You can find the code of the demo on GitHub.
Create a new .NET 6 console application using your favorite IDE or the command line. First, add install the following two NuGet packages
Next, create a new class, that will read the appsettings file and also the NETCORE_ENVIRONMENT environment variable.
The NETCORE_ENVIRONMENT variable is the default variable to configure your environment in .NET. This variable contains values such as Development or Production and can be used to read a second appsettings file for the specific environment. For example, in production, you have a file called appsettings.Production.json which overrides some values from the appsettings.json file.
Next, add a new file, called appsettings.json, and add the following code there:
This file contains a username and password. Values that should never be checked into source control!
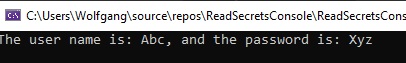
Lastly, add the following code to your Program.cs file:
This code creates a new instance of SecretAppsettingReader and then reads the values from the appsettings.json file. Start the applications and you should see the values printed to the console.
Add Secrets to your Application
The application works and reads the username and password from the appsettings file. If a developer adds his password during the development, it is possible that this password gets forgotten and ends up in the source control. To mitigate accidentally adding passwords to the source control, .NET introduced secrets.
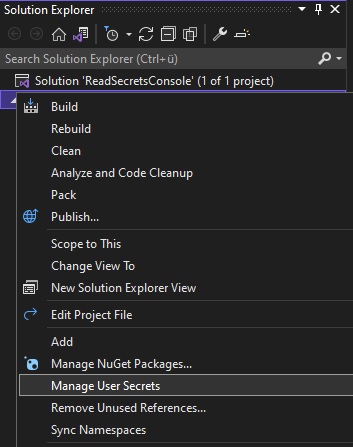
To add a secret, right-click on your project and then select “Manage User Secrets” in Visual Studio.
This should create a secrets.json file and add the Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration.UserSecrets NuGet package. Sometimes Visual Studio 2022 doesn’t install the package, so you have to install it by hand with the following command:
You can use the secrets.json file the same way as you would use the appsettings.json file. For example, add the “MySecretValues” section and a new value for the “Password”:
There is one more thing you have to do before you can use the secrets.json file. You have to read the file using AddUserSecrets in the SecretAppsettingReader file:
The AddUserSecrets method takes a type that indicates in what assembly the secret resides. Here I used Program, but you could use any other class inside the assembly.
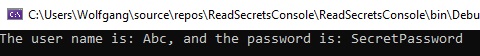
Start the application and you should see that the password is the same value as in the secrets.json file.
When you check in your code into Git, you will see that there is no secrets.json file to be checked in. Therefore, it is impossible to check in your secrets like passwords.
Conclusion
Secrets help developers to keep their repositories free of passwords and other sensitive information like access tokens. .NET 6 allows you to set up these secrets with only a couple of lines of code.
You can find the code of the demo on GitHub.


Comments powered by Disqus.